Recursion
Home * Programming * Algorithms * Recursion
Recursion is a technique to define a function, or process of repeating objects, in a self-similar way. In computer science it is a method or algorithm where the solution to a problem depends on solutions to smaller instances of the same problem.
Contents
Sample
In the Tower of Hanoi puzzle to move N disks from peg A to C can be reduced to three sub problems:
- Moving N-1 disks from peg A to intermediate peg B
- Move the largest Disk N from peg A to target C
- Finally move the N-1 parked disks from B to C
Recursive Definitions
A recursive definition of an object refers inductive terms of itself. A function set need to specify the function for some discrete values like zero, one or empty (base case), and to reduce all other cases by divide and conquer toward the base case. Recurrence relation is an equation that recursively defines a sequence of symbols or numbers [2].
Some more or less computer chess related examples ...
PGN Syntax
The BNF-like Syntax of the Portable Game Notation by Steven Edwards contains some recursive definitions, most tail recursion for iteration of games, and tag-pairs and elements inside a game [3] :
<PGN-database> ::= <PGN-game> <PGN-database>
<empty>
<tag-section> ::= <tag-pair> <tag-section>
<empty>
<element-sequence> ::= <element> <element-sequence>
<recursive-variation> <element-sequence>
<empty>
<recursive-variation> ::= ( <element-sequence> )
Index of PV-Array
An index of a Triangular PV-Table may be defined recursively that way ...
index(0) = 0 index(ply+1) = index(ply) + N - ply
...which can be trivially transformed from tail recursion to iteration, finally applying a summation:
index(ply) = ½ ply (2N + 1 - ply )
Population Count
The recursive definition of population count (number of one-bits in a computer word i. e. a bitboard) can be transformed to iteration as well, but lacks an arithmetical sum-formula:
popcnt(0) = 0 popcnt(n) = popcnt(n ÷ 2) + (n mod 2)
Infix Expression
Formal syntax of programming languages likely contain recursive definitions, i. e. parsing of arithmetical (and/or boolean) infix notation therefor implies indirect recursion, as demonstrated in following example with constants and elementary arithmetic only, which might even evaluated at compile time:
Terminal and none terminal symbols of a variant of BNF below are embedded in ' ' resp. < >.
<expression> ::= <term> [ {'+' | '-'} <term> ]...
<term> ::= <factor> [ {'*' | '/'} <factor> ]...
<factor> ::= <constant> | '(' <expression> ')'
Implementation
In procedual programming, recursion is done by a procedure aka subroutine, method or function, which calls itself if no base case is determined, utilizing the processor stack. One has to take care the nesting is not too deep or infinite, which yields in a Stack overflow and abnormal program termination or crashing.
Recursive Data types
Recursive data types contain references (i. e. pointer in C) to objects of the same type to build directed graphs, such as linked lists or trees.
Recursive Algorithms
Searching
Tree-like data structures which are traversed in depth-first manner can be implemented with recursion using a stack of nodes. Minimax and alpha-beta are typical examples of indirect recursive routines, where Min calls Max and Max calls Min, and Negamax turns the indirect recursion to a direct one. While tail recursion or primitive recursion can easily turned into iterative solutions, it is more complicated for not primitive recursion. However, recursion can turned to a non-recursive version based on the use of continuations, see Iterative Search.
Knuth and Moore already introduced an iterative solution of Alpha-Beta in 1975 [4] :
It is interesting to convert this recursive procedure to an iterative (non-recursive) form by a sequence of mechanical transformations, and to apply simple optimizations which preserve program correctness. The resulting procedure is surprisingly simple, but not as easy to prove correct as the recursive form.
So called recursive pruning, especially null move pruning, or extensions refers to the fact that these events may occur multiple times inside a variation or path of the (recursive) search process.
Sorting
A well-known sorting algorithm is Quicksort developed in 1960 by C. A. R. Hoare. It recursively partitions and sorts two sub-lists from a list, whose elements are either less and greater a chosen pivot element. However, for move ordering to sort move lists in alpha-beta, most chess programmer use a selection sort to pick a move with best assigned score, since the effort to sort other moves may needless in case of a beta-cutoff.
Visualization of the quicksort algorithm [5]
See also
- Alpha-Beta
- Backtracking
- De Bruijn Sequence Generator
- Depth-First
- Iteration
- Iterative Search
- Jamboree
- Minimax
- Negamax
- Parallel Alpha-Beta in Cilk
Publications
- John McCarthy (1960). Recursive Functions of Symbolic Expressions and Their Computation by Machine, Part I, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, pdf
- V. I. Sobel'man, Mikhail R. Shura-Bura (1962). Realization of recursive procedures in the language of AlGOL-60. (Реализация Рекурсивных Процедур В Языке Алгол-60) Zhurnal Vychislitel'noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki, Vol. 2, No. 2
- Michael Levin (1963). Primitive Recursion. AIM-055, reprint available from DSpace at MIT
- Craig A. Finseth (1980). Something is Missing (Implementing recursion and stacks in BASIC). The Best of Creative Computing Volume 3 » Basic
- Ingo Althöfer (1988). On the Complexity of Searching Game Trees and Other Recursion Trees. Journal of Algorithms, Vol. 9, No. 4
- Ingo Althöfer (1991) On pathology in game tree and other recursion tree models. Habilitation Thesis, University of Bielefeld
- Donald Knuth (1991). Textbook examples of recursion. arXiv:cs/9301113
- Raymond Smullyan (1993). Recursion Theory for Metamathematics. Oxford University Press [6]
- Richard J. Lorentz (1994). Recursive algorithms. Intellect Books
- Kevin Coplan (1998). Synthesis of Chess and Chess-like Endgames by Recursive Optimisation. ICCA Journal, Vol. 21, No. 3
- David Slate, Peter W. Frey (2009). Recursive Binary Partitioning, Old Dogs with New Tricks, KDD Conference 2009, slides as pdf [7]
Forum Posts
- Was ist rekursiv? irrelevant! by Helmut Richter, sci.lang, September 29, 1998
- how to print tree non-recursively by Daniel Shawul, CCC, February 24, 2012 » Search Tree, Iteration
- Recursive DTS-like search algorithm by Peter Österlund, CCC, July 24, 2013 » Texel, Parallel Search
External Links
Recursion
- Recursion from Wikipedia
- Recursion by Weisstein, Eric W. from Wolfram MathWorld
- Recursion (computer science) from Wikipedia
- Recursive acronym from Wikipedia
- Recursive data type from Wikipedia
- Recursive definition from Wikipedia
- Recursion in Nature, Mathematics and Art by Anne M. Burns
- Recursion theory from Wikipedia
Recursive Functions
Ackermann Function
- Ackermann function from Wikipedia » Wilhelm Ackermann
- Ackermann Function by Weisstein, Eric W. from Wolfram MathWorld
McCarthy 91-Function
Introduced by Zohar Manna, Amir Pnueli and John McCarthy in 1970.
- McCarthy 91 function from Wikipedia
- McCarthy 91-Function by Weisstein, Eric W. from Wolfram MathWorld
Tak
Self-reference
Fractals
- Hilbert curve from Wikipedia » David Hilbert
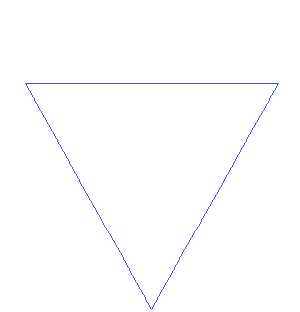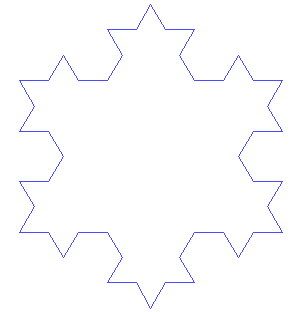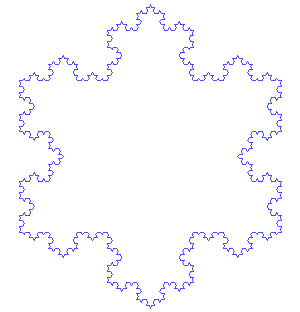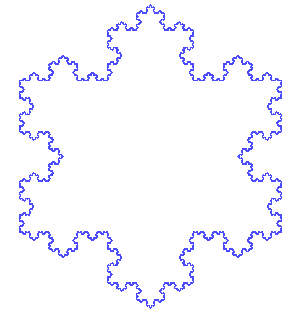
- Koch snowflake from Wikipedia » Helge von Koch
- Peano curve from Wikipedia » Giuseppe Peano
- Sierpinski triangle from Wikipedia » Wacław Sierpiński
Misc
- Divide and conquer algorithm from Wikipedia
- Eternal return from Wikipedia
- Lambda Calculus from Wikipedia
- Knights of the Lambda Calculus from Wikipedia » Alonzo Church
- Mathematical induction from Wikipedia
- Recurrence relation from Wikipedia
- Reentrant (subroutine) from Wikipedia
- Turing completeness from Wikipedia
- Return to Forever, San Sebastian Jazz Festival, July 25, 2008, YouTube Video
References
- ↑ Tetrahedron in Bottrop, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, part of The Industrial Heritage Trail, Image by Gerd Isenberg, April 08, 2017. The design is reminiscent of the Sierpinski tetrix : placing four half-size tetrahedra corner to corner and adding an octahedron in the middle, a full-size tetrahedron is formed; this process can be repeated recursively to form larger and larger tetrahedra, from Tetrahedron in Bottrop from Wikipedia, Category:Tetraeder Bottrop - Wikimedia Commons, Halden im Ruhrgebiet (German)
- ↑ Hofstadter sequence from Wikipedia
- ↑ Standard: Portable Game Notation Specification and Implementation Guide by Steven Edwards, 18: Formal syntax
- ↑ Donald Knuth, Ronald W. Moore (1975). An analysis of alpha-beta pruning. Artificial Intelligence, Vol. 6, No. 4
- ↑ Quicksort from Wikipedia
- ↑ Metamathematics from Wikipedia
- ↑ Results of the KDD cup 2009